Breast imaging looks for abnormalities in breast tissue. Often, patients receive these services as part of a routine screening for breast cancer. Not everyone has the same risk level, however, which is why your ideal screening method may be different from someone else’s. Here’s a look at the various breast imaging techniques available today.
Mammography
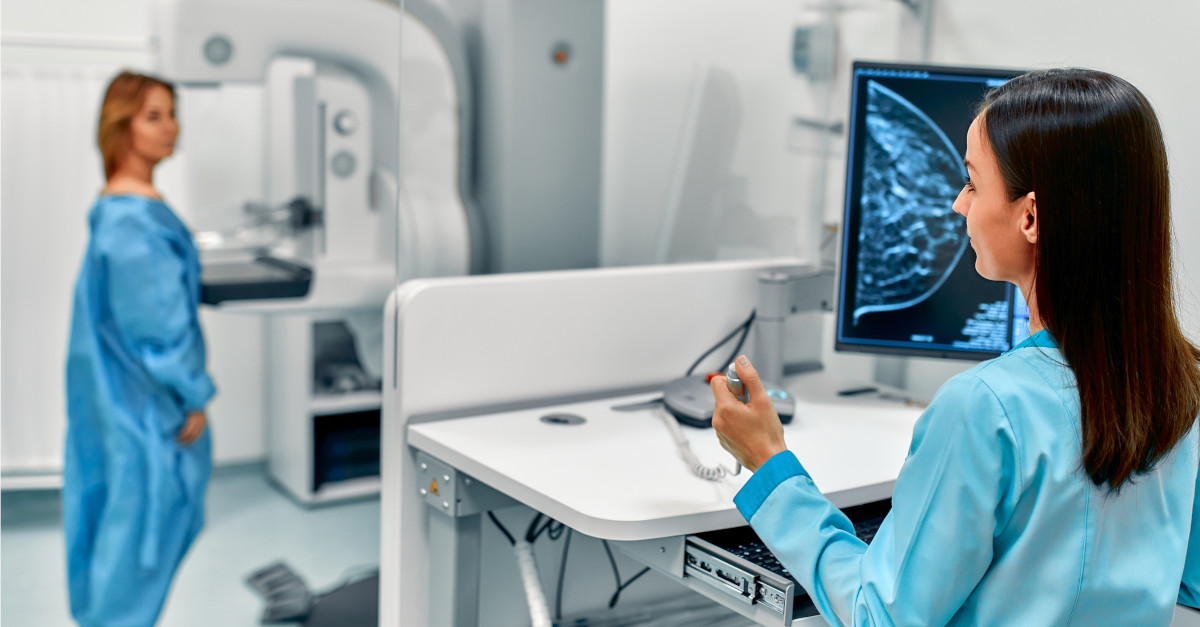
Mammograms are medical imaging exams that use low-dose X-rays to capture images of compressed breast tissue. The American Cancer Society notes that these screenings are often able to find or detect breast cancer early, “when it’s small and even before a lump can be felt.”
In traditional mammography, images of breast tissue are two-dimensional. A little over a decade ago, the FDA approved 3D mammography devices to capture far more images of the tissue. Whereas 2D mammograms capture only four angles of the breast, 3D mammography captures many layers of tissue, providing a more thorough picture and potentially revealing abnormalities that wouldn’t appear in 2D imaging.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends screening mammography every one to two years beginning at age 40 for women of average risk. While you should discuss your individual risk factors with your doctor to reach an informed decision, the National Cancer Institute also offers a Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool which you may wish to use in the meantime. It considers factors such as personal medical and reproductive history, as well as the medical history of first-degree relatives.
Cardinal Points Imaging offers 3D Mammography Exams in Raleigh, NC and surrounding areas!
MRI
Traditional MRI
While routine breast cancer screenings are important for all women over the age of 40, they’re even more critical for patients with a higher risk. Factors linked to an elevated breast cancer risk include
- Prior radiation treatment to the chest.
- A personal or family history of breast cancer.
- A BRCA1 or BRCA2 inherited gene mutation.
Other gene mutations and medical conditions, such as lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS), may also be considered.
For these patient populations, a breast MRI may be recommended as a screening protocol. MRI uses magnetic and radio waves to create detailed, cross-sectional pictures of breast tissue. In patients with a higher than average risk, breast MRI used with mammography is better than mammograms alone at detecting breast cancer.
Abbreviated Breast MRI
While the best imaging services for women with average and high risks are clear, the guidelines for women with an intermediate risk are less so. For example, while a breast MRI could be beneficial for patients with moderate-risk gene mutations, their insurance may not offer coverage for the service if they don’t meet certain criteria.
For this group, abbreviated breast MRI is a low-cost yet effective alternative. It can be completed in a fraction of the time required for a traditional MRI, takes less time to interpret, and is therefore more affordable.
Whether your doctor recommends a mammogram or MRI, the breast care center at Cardinal Points Imaging in Raleigh, NC, is your source for quality imaging services performed by caring, attentive staff. Find out more about our women’s imaging options, including 3D mammograms and abbreviated breast MRI. Or schedule an appointment by calling (919) 877-5400.